Table of Contents
Biomes Meaning
A biome is a large area where different living things, like plants and animals, thrive in a specific climate. The Earth has many diverse environments, grouped into biomes based on temperature, weather, and adaptations. The term “biome” was introduced in 1916 by ecologist Frederic Edward Clements. Biogeographers divide the Earth into distinct areas with similar plants and animals. For example, tropical evergreen forests in the Congo Basin and South America look alike but may have different species. However, they share common characteristics, which define them as the same biome. So, a biome is a large area with similar life forms and consistent environmental conditions.
Read More: Climatology
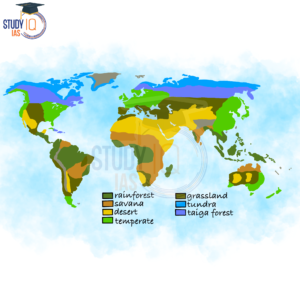
Biomes of the World
Biomes are large ecosystems characterized by distinct climates, flora and fauna. Some of the main Biomes of the World include:
Biomes Factors Affecting
Below are the factors affecting biomes.
Temperature and Precipitation
Temperature and precipitation are important factors that influence biome characteristics and distribution. Temperature and precipitation variations affect various aspects of biomes, such as plants. Biomes with low precipitation and extreme temperatures have short growing seasons and poor soil. Thus, fewer types or quantities of plants and animals will grow under these conditions.
Latitude
Differences in biomes can also be caused by latitude. This depends on their position in relation to the Equator. The temperature will vary depending on which angle receives sunlight. For example, biomes in high latitudes farthest from the Equator, such as taiga and tundra, receive the least sunlight and have lower temperatures. However, biomes in the middle latitudes between the poles and the Equator, such as temperate deciduous forests, receive more sunlight and have moderate temperatures.
Elevation
Elevation refers to the height of land above sea level, and it has a significant impact on biomes. The change occurs as the atmosphere thins at higher elevations, retaining less heat. Elevation influences precipitation because moist clouds rise and release rain or snow.
Read More: Equatorial Climate Region
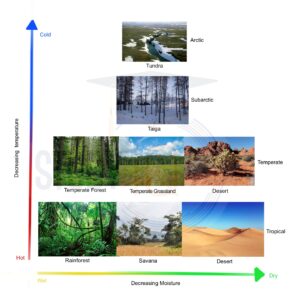
Biomes Types
There is a close relationship between climate types and the world’s distribution of biomes. The biomes are divided into three major types based on climate type.
- These are Tundra Biome,
- Temperate Biome, and
- Tropical Biomes. Further, these three biomes are divided into sub-types based on dominant vegetation. Below are the important biomes of the world.
Read about: Coral Reef
Tropical Biomes
Tropical biomes are discussed below:
- Tropical Evergreen Forest
- Monsoon Deciduous Forests
- Savanna Biome
- Desert Biome
- Mediterranean Biome
Tropical Evergreen Forest
Tropical evergreen forests are thick and layered, filled with many kinds of plants and animals. They grow in places that get a lot of rain, over 200 cm each year. These forests are so dense that sunlight hardly reaches the ground, and they have many different tree species.
Distribution
The tropical evergreen forests are found between 5° and 10° north and south of the equator. Its greatest range is located in the Amazon Basin (South America), Congo Basin (Africa), and Indo-Malaysian region (Java, Sumatra, Borneo, Malaysia, and Guinea).
Climate
Tropical evergreen forests thrive in a climate that is consistently warm, frost-free, and mostly wet throughout the year. The monthly average temperature is always around 27°C. The daily temperature is moderated by cloudiness and heavy precipitation. Plants grow abundantly in such situations.
Plant and Animal Species
The tropical evergreen rainforest has the most plant species, with 6,000–7,000 in Africa, 20,000 in Malaysia, 40,000 in Brazil, and 2,000 in Panama. It features tall, closely spaced trees and dense shade from the canopy. Animals include herbivores like sloths and tapirs, carnivores like jaguars, and many colorful birds and butterflies. This biome is the most productive in the world, contributing 40% of global biological productivity.
Human and Tropical Evergreen Forests
The forests have few people and limited economic activity. Most of the local communities are hunter-gatherers, while some practice shifting cultivation. Many tropical rainforests have been cleared for logging or farming.
Read about: Continental Drift Theory
Monsoon Deciduous Forests
The biome of any open woodland in tropical areas has a long dry season followed by a season of heavy rainfall, also known as monsoon forest or tropical deciduous forest.
Distribution
It is found in latitudes ranging from 5° to 30° latitude on either side of the equator. They are most developed in India, Burma, Thailand, Laos, Cambodia, parts of Vietnam, south China, and northern Australia.
Climate
The climate is characterized by tropical rainy seasons and dry seasons. The average temperature in summer ranges from 27°C to 30°C. The average annual rainfall is 1500mm.
Plant and Animal Species
The natural vegetation of tropical monsoon lands is determined by the rainfall received during the summer. Trees are deciduous due to the prolonged dry period. They shed their leaves to survive the drought period. There are fewer plant species than evergreen forest biome. Sal, teak, and bamboo are major plant species.
Major animals found in these forests include rhinos, elephants, tigers, wild buffalo, etc. Several bird species are also found.
Human and Tropical Monsoon Deciduous Forests
The biome has the largest human population in the world. Agriculture is the people’s primary economic activity. Rice, cane sugar, jute, and other major crops are grown.
Read about: Land Reforms in India
Savanna Biome
The savanna biome is frequently described as grassland with scattered trees or clusters of trees. The savanna’s lack of water makes it difficult for tall plants like trees to grow. Savanna grasses and trees have adapted to life with little water and high temperatures.
Distribution
The savanna climate, also known as the Sudan climate, is a mix between equatorial forests and hot deserts. It is mostly found in the tropics, especially in Sudan, where the wet and dry seasons are clear. This climate stretches from West Africa to East and southern Africa, north of the Tropic of Capricorn. In South America, savannas are found in the llanos of the Orinoco basin and the Campos of the Brazilian Highlands. They can also be seen in northern Australia.
Climate
Savanna’s climate is distinguished by distinct wet and dry seasons. There is also no distinct rainy season, as there is in the monsoon climate. The average annual temperature is higher than 18° C. The days are hot, and the nights are cold.
Plant and Animal Species
In the savanna biome, trees are spaced far apart due to low soil moisture, allowing grasses to grow thickly below. This gives the area a park-like look. Common plants include baobab, palm, and eucalyptus. The African savanna has many grazing animals like buffalo, zebras, giraffes, and elephants. In Australia, kangaroos are the main animals.
For people, many tribes depend on savanna lands for their economy. The Masai are pastoralists, while the Hausa in northern Nigeria are settled farmers, although agriculture is still not very advanced.
Read about: List of Biosphere Reserves in India
Desert Biome
A desert biome is a collection of habitats that develop in arid (dry) environments as a result of little or no rainfall (50 cm per year).
Distribution
The major hot deserts of the world are located on the western coasts of continents between latitudes 15º and 30º N and S. They include the Sahara Desert (3.5 million square miles), the Great Australian Desert, the Arabian Desert, the Iranian Desert, the Thar Desert, the Kalahari Desert, and the Namib Desert. The desert in North America stretches from Mexico into the United States. It is known by various names such as the Mohave, Sonoran, Californian, and Mexican Deserts. The Atacama or Peruvian Desert is the driest desert in South America. It receives less than 2 cm of rain per year.
Climate
The deserts are some of the hottest places on Earth, with high temperatures all year. In the hot deserts, the average summer temperature is around 30°C. In the Sahara, the highest shade temperature recorded is 58°C at Al Azizia, Libya. The diurnal temperature range in the deserts is large. Rainfall is scanty- below 30 cm.
Plant and Animal Species
Desert plants are adapted to save water and are called xerophytes. They have thick stems and spines, like cacti. Common animals in deserts include arthropods, reptiles, birds, and small mammals. Large animals are rare. Small rodents, foxes, and rabbits are more common. For example, black-tailed jackrabbits have long ears to help release extra heat from their bodies.
Human and the Desert Biome
Deserts have always been home to different groups of people, including:
- Primitive hunters and gatherers (like the Bushmen and Bindibu)
- Nomadic herders (like the Tuaregs, Gobi Mongols, and Bedouins)
- Caravan traders
- Settled farmers
- Mining settlers
Temperate biomes are located between the tropics and the poles. They have moderate differences between summer and winter, allowing for various habitats, including forests and grasslands.
Read about: Mangrove Forests in India
Mediterranean Biome
Mediterranean vegetation, is any dense scrubland composed of broad-leaved evergreen shrubs, bushes, and small trees growing in regions between 30° and 40° north and south latitudes.
Distribution
It is found between 30°-40° latitudes in both hemispheres. They are found in western parts of the continents. It includes the European lands bordering the Mediterranean Sea, central and southern California in the USA, central Chile in South America, north-western coastal lands of Africa bordering the Mediterranean Sea, coastal zones of Western and Southern Australia, western Turkey, Syria, western Israel and Lebanon.
Climate
It is characterized by a Mediterranean type of climate. The summers are warm and dry and the winters are cool. Most of the rainfall occurs during the winter. The average temperature in winter ranges from 5-10C, while the average summer temperature ranges from 20-27C. Average rainfall range from 370mm to 650mm.
Plant and Animal Species
The Mediterranean biome is mainly made up of trees and shrubs. The plants have small, thick leaves that help them save water during dry summers. These are called sclerophylls and include holm oaks, olive trees, and cypresses, as well as herbs like rosemary and thyme.
Animals like wild goats, sheep, and lynx also live here.
Humans use this region for farming fruits, growing cereals, winemaking, and mining.
Read about: National Parks in Idia
Temperate Grassland Biome
Temperate grasslands experience cold winters and warm, rainy summers. Each year, the grasses die back to their roots, which are protected by the soil from the cold and dry conditions. Because there is not much rainfall, you might find a few trees near the streams.
Distribution
Temperate grasslands are found in the interior of continents in the northern hemisphere and on the southeastern edges in the southern hemisphere. They have different names in various regions:
- Eurasia: Known as steppes, stretching from the Black Sea to Manchuria in China.
- North America: Called prairies, located between the Rocky Mountains and the Great Lakes.
- Argentina and Uruguay: Referred to as pampas.
- South Africa: Known as velds, between the Drakensberg mountains and the Kalahari desert.
- Australia: Called downs, found in the Murray-Darling basins of South Australia.
Climate
Temperate grasslands in the northern hemisphere have extreme temperatures in summer and winter, while those in the southern hemisphere have a milder climate due to their proximity to the sea. Most rainfall occurs in summer.
Plants: These areas are covered in treeless grasslands made up of perennial grasses.
Animals: Common animals include antelopes, wild asses, horses, wolves, kangaroos, emus, and dingoes.
Human Impact: Grasslands have been turned into large wheat fields, making them major grain-producing areas. They also serve as grazing lands for many animals.
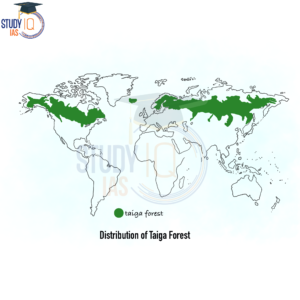
Taiga Biome
The taiga is a cold-weather subarctic forest. The subarctic region of the Northern Hemisphere is located just south of the Arctic Circle. The taiga is located between the tundra and temperate forests to the north and south, respectively. Taigas can be found in Alaska, Canada, Scandinavia, and Siberia.
Distribution
In the northern hemisphere, it is located in the sub-arctic region, south of the Arctic Circle. It is found in Alaska of USA, Canada, Scandinavia, and Siberia. They are also known as the Boreal forest Biome.
Climate
The taiga biome has very low average temperatures, usually between -5 and 5 °C. Winters are long and cold, while summers are short and warm, with little rainfall.
Plants: The main plants are coniferous trees, which have needle-like leaves and stay green all year. Common types include pine, fir, spruce, and larch. Some deciduous trees, like alder, birch, and poplar, can also be found in areas cleared by humans.
Animals: Animals in the taiga are well adapted to the cold. Common species include moose, lynx, bears, and Siberian tigers. Many birds migrate south during the harsh winter.
Humans and the Taiga Biome
Forests are cleared for lumbering. There is little agriculture because few crops can survive in harsh climates. Siberian Samoyeds, Yakuts, and some Canadians engage in hunting, trapping, and fishing.
Tundra Biome
The tundra ecosystem has no trees and is covered in snow for most of the year. It is found in cold areas with little rainfall. Because of its tough climate, tundra is often at lower altitudes and is similar to deserts. The word “tundra” comes from Finnish, meaning “deserted land. “This means that the tundra region has the least amount of vegetation and the most extreme polar or arctic climate. It is further classified as
- arctic tundra biome and
- alpine tundra climate (which is found over high mountains of tropical and temperate areas).
Distribution
Polar climates and vegetation are found in the northern hemisphere, north of the Arctic Circle. Ice caps are mainly in Greenland and high-altitude areas. The ground is always covered in snow here. In the lowlands, tundra plants grow during the few months when the ice melts. This includes places like Greenland’s coast, northern Canada and Alaska, and the Arctic coastal area of Eurasia.
Climate
It has a very low average temperature throughout the year. Even in its warmest month, June, the temperature usually does not go above 10°C. In mid-winter (January), temperatures can drop to -35°C, and it’s even colder in the interior areas. Winters are long and harsh, while summers are cool and brief. Precipitation is primarily in the form of snow. It falls in winter and is blown around during snowstorms.
Plant and Animal Species
In the tundra, plants grow during a short summer with long days and little to no nights. The plants are usually small, including grasses, mosses, lichens, and shrubs. They thrive when marshy landforms as temperatures rise above freezing and a thin layer of ice melts, but the deeper permafrost stays frozen, creating wet conditions. Animal life is limited due to the harsh climate, but you can find reindeer, wolves, foxes, musk-oxen, arctic hares, seals, and lemmings. Human activity in the tundra is mostly along the coast. The few people who live here are semi-nomadic and adapt to the tough environment. The discovery of minerals has led to some new settlements, along with support for indigenous groups like the Eskimos, Lapps, and Samoyeds.
Biomes UPSC
The terrestrial portion of the biosphere is divided into large sections known as biomes, which are defined by climate, flora, animal life, and general soil type. There are no two identical biomes. The climate determines the boundaries of each biome, as well as the abundance of plants and animals that inhabit it. The most important climatic elements are temperature and precipitation.
The terrestrial portion of the biosphere is divided into large sections known as biomes, which are defined by climate, flora, animal life, and general soil type. There are no two identical biomes. The climate determines the boundaries of each biome, as well as the abundance of plants and animals that inhabit it. The most important climatic elements are temperature and precipitation. This article will explain Biome, which will help you prepare for the UPSC Civil Service exam’s Environment syllabus. This article will explain Biome, which will help you prepare for the UPSC Civil Service exam’s Environment syllabus.


 El Nino and La Nina and its Impact on In...
El Nino and La Nina and its Impact on In...
 Manganese Ore, Uses, Properties, Importa...
Manganese Ore, Uses, Properties, Importa...
 Faraizi Movement, History, Founder, Begi...
Faraizi Movement, History, Founder, Begi...




















