Table of Contents
Bengaluru Terror Attack
- On March 1, an explosion occurred at the bustling Rameshwaram Cafe in Bengaluru’s Whitefield area, injuring at least nine people.
- Karnataka Chief Minister Siddaramaiah ruled out a gas leak, stating that CCTV footage revealed a man placing a bag in the cafe, indicating the possibility of an improvised explosive device (IED).
Details about IED Blast in Rameshwaram Cafe
A disturbing incident unfolded in Bengaluru’s Whitefield area as an explosion ripped through the popular Rameshwaram Cafe, injuring at least nine people. Initial reports suggest the blast was caused by an improvised explosive device (IED) placed inside a bag left at the cafe.
The explosion occurred around 1 PM, a peak lunchtime hour, when the cafe was likely bustling with patrons. Visuals from the scene depict the cafe in disarray, with shattered glass and debris scattered around. Emergency personnel, including police, firefighters, and bomb disposal squads, swiftly arrived at the location to secure the area, provide medical assistance to the injured, and commence investigations.
Karnataka Chief Minister Siddaramaiah confirmed the blast was caused by an IED and condemned the act in a statement. He further informed that CCTV footage captured a man placing the bag inside the cafe, and a search for the suspect is underway.
The motive behind the attack remains unclear at this time, and authorities are conducting a thorough investigation. This incident has undoubtedly caused fear and apprehension among the residents of Bengaluru, raising concerns about public safety.
Understanding IEDs
Definition
- An IED, or improvised explosive device, is essentially a home-made bomb.
- According to the United States Department of Homeland Security, IEDs can vary in form, from small pipe bombs to sophisticated devices capable of causing significant damage and loss of life.
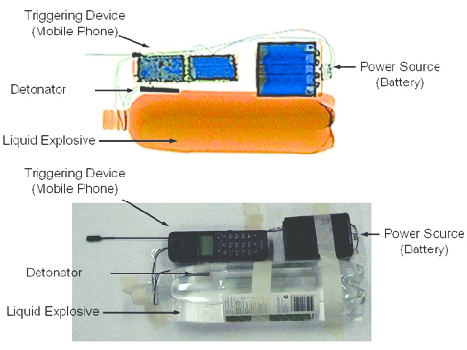
Components
- Each IED consists of several basic components, including an initiator or triggering mechanism, a switch to arm the explosive, a main charge for the explosion, a power source (typically electronic), and a container.
- IEDs may also contain additional materials such as nails, glass, or metal fragments to increase the damage caused by the explosion.
Materials Used
- Common materials used to build IEDs include fertilizers like ammonium nitrate and urea nitrate, gunpowder, and hydrogen peroxide.
- Restrictions on carrying liquids aboard commercial aircraft stem from the potential for passengers to create IEDs by mixing commonly available liquids.
Damage Caused by IEDs
- The extent of damage caused by an IED depends on factors such as its size, construction, placement, and the presence of high explosives.
- While smaller IEDs may be easier to conceal and deploy, they generally cause less damage compared to larger ones.
Historical Use
- IEDs have been used in various incidents globally, including the 1993 Mumbai serial blasts, the 2008 Jaipur blasts, the 2006 Jama Masjid bombings, and the 2013 Bodh Gaya bombings.
- They are also commonly employed by insurgent groups such as Maoists and Kashmiri militants.


 Utkal Divas 2025: Odisha Foundation Day ...
Utkal Divas 2025: Odisha Foundation Day ...
 List of Military Exercises of India 2024...
List of Military Exercises of India 2024...
 GPS Spoofing and Its Impact in India: A ...
GPS Spoofing and Its Impact in India: A ...





















