Table of Contents
- The Barak River originates from the Japvo mountain in the Manipur hills.
- Before entering Bangladesh, it flows through the northeastern states of Manipur, Nagaland, Mizoram, and Assam.
Barak River Tributaries
- The river has several tributaries, including:
- Jiri, Dhaleswari, Singla, Longai, Sonai, and Katakhal.
Importance and Geography
- The Barak River is the second-largest river in Northeast India, following the Brahmaputra.
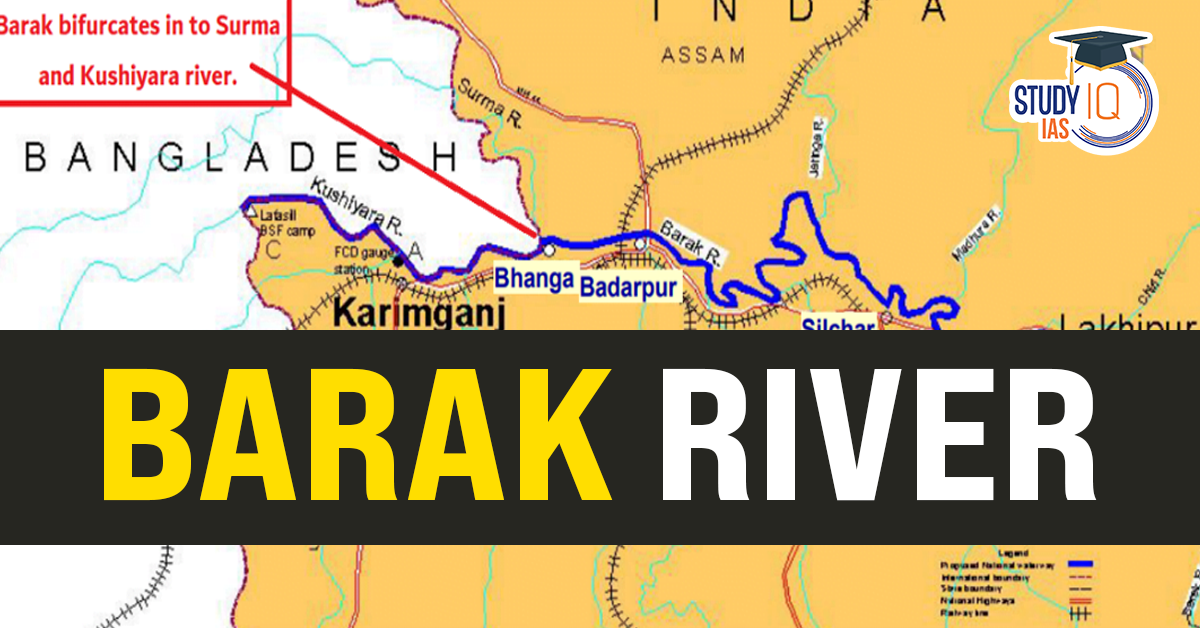
- In Bangladesh, it splits into two branches, the Surma and Kushiyara, eventually merging to form the Meghna River.
- The Meghna receives the combined flow of the Ganga and Brahmaputra, making it a major river system.
Navigational Significance
- A portion of the river between Lakhipur and Bhanga is navigable and designated as National Waterway 6 (NW-6), enhancing regional connectivity.
Biodiversity
- The Gangetic River Dolphin (Susu), an endangered species, is found in the Barak River, underscoring its ecological importance.
Hydro Projects
- Major hydroelectric and irrigation projects associated with the river include:
- Tipaimukh Dam Project (a controversial dam for flood control and hydroelectricity).
- Tista Champamati and Dhansiri barrages, contributing to irrigation and water management.

 National Technology Readiness Assessment...
National Technology Readiness Assessment...
 Justice Mission-2025: China’s Live-Fir...
Justice Mission-2025: China’s Live-Fir...
 Suryastra: First Made-in-India Long-Rang...
Suryastra: First Made-in-India Long-Rang...

























