Table of Contents
Context: Recent research has introduced a groundbreaking technology that enables sound to be heard only in specific locations, creating “audible enclaves.”
About Audible Enclaves
- Audible enclaves are localized pockets of sound that can be heard only in a specific area, while remaining completely silent elsewhere.
- This means sound can be directed to a single person or location without disturbing others nearby.
| What is Sound? |
|
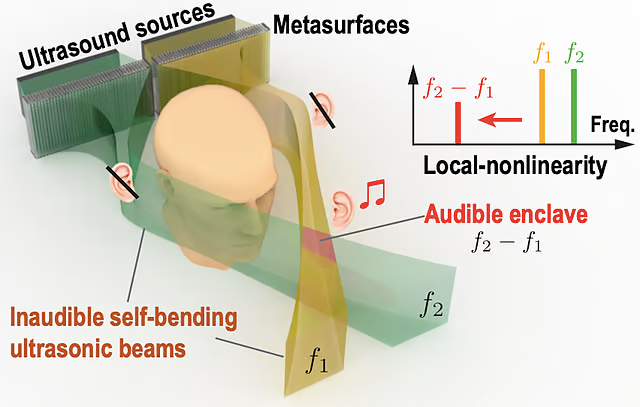
How Audible Enclaves Work?
Using Ultrasound as a Carrier
- Ultrasound waves (above 20 kHz) are inaudible to humans but can carry normal sound through the air.
- These ultrasound waves can be shaped and controlled to deliver sound only where needed.
Nonlinear Acoustics – Creating Sound at a Specific Spot
- Normally, sound waves mix linearly (just adding together).
- However, at high intensities, sound waves interact nonlinearly, producing new frequencies that weren’t there before.
- Scientists use two ultrasound beams at different frequencies that are silent on their own but generate audible sounds only where they intersect.
Bending Ultrasound Waves
- Normally, sound waves travel in straight lines.
- By using acoustic metasurfaces (specialized materials that shape sound waves), scientists can bend ultrasound beams to meet at a specific target, creating an audible enclave in that location.
Difference Frequency Generation
- When two ultrasound beams of slightly different frequencies overlap, they create a new sound at the difference between their frequencies.
- Example:
- One beam at 40 kHz
- Another beam at 5 kHz
- Difference = 5 kHz (500 Hz), which humans can hear
- This means sound only exists at the point where the waves meet, and nowhere else.
Potential applications of Audible Enclaves
- Private Audio: Listen to music, podcasts, or calls without headphones, and without disturbing others.
- Personalized Audio in Public Places: Museums, libraries, and offices can provide location-based audio without speakers.
- Noise Control: This can be used to create silent zones by cancelling unwanted noise.
- Confidential Conversations: Military, corporate, and security settings can ensure private discussions in open spaces.
- Car Audio: Passengers can listen to music without distracting the driver.


 Advanced Air Defence Radars: Types, Comp...
Advanced Air Defence Radars: Types, Comp...
 Ion Chromatography, Working and Applicat...
Ion Chromatography, Working and Applicat...
 Broadly Neutralising Antibodies (bNAbs):...
Broadly Neutralising Antibodies (bNAbs):...

























