Table of Contents
Context: The Asian Development Bank (ADB) has revised its GDP growth forecast for India, raising it to 7% for the current fiscal year (2023-24) from its previous projection of 6.7%.
Asian Development Outlook Report Findings
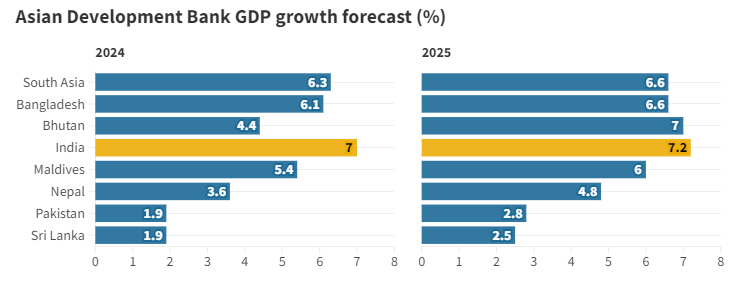
GDP Growth Forecast
- 2023-24: India’s GDP growth is forecasted at 7.6%.
- 2024-25: Expected slowdown in GDP growth to 7%.
- 2025-26: Projected improvement in GDP growth to 7.2%.
Inflation Projections
- Retail inflation is expected to decrease to 4.6% in 2024 and to 4.5% in 2025-26.
- Food inflation, described as ‘persistent,’ is projected to reduce to 5.7% in 2024 due to farm output returning to normal trends.
Agricultural and Rural Economy
- A normal monsoon forecasted for 2024 is anticipated to boost rural consumption.
- Rural consumption had been subdued last year due to erratic rainfall impacting agriculture.
- Increased demand for work under the Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Act indicated stress from last year’s poor agricultural conditions.
Economic Growth Drivers
- Consumption increase and continuous investment growth are key drivers of India’s robust economic growth.
- Public and private sector investment along with gradual improvements in consumer demand, especially in rural areas, are expected to stimulate growth.
- Exports are expected to be muted in 2024 but improve by 2025-26.
Consumer Demand and Urban Economy
- Rising incomes are expected to enhance consumer demand.
- Improved confidence among urban consumers and a gradual improvement in urban labour markets are likely to boost demand in urban areas.
Current Account Deficit and Imports
With rising domestic demand, imports are expected to increase, potentially widening the Current Account Deficit to 1.7% of GDP in 2024 and 2025.
Investment and Foreign Direct Investment (FDI)
FDI inflow is expected to remain muted in the near term due to tight global financial conditions but is anticipated to pick up in 2025-26 with more industry and infrastructure investments.
Risks and Outlook
The economic outlook depends on maintaining price and financial market stability.
- Downside risks include global shocks such as spikes in crude oil and energy prices, leading to higher global inflation and tighter financial conditions.
- Domestic risks involve potential underperformance in agriculture due to weather shocks, which could affect demand and inflation.
- Upside risks include faster-than-expected FDI, particularly in manufacturing, and better-than-expected global growth, which could boost exports and overall growth.
Regional Context
India constitutes 80% of South Asia’s GDP and is the fastest-growing sub-region in South Asia, expected to grow at 6.3% in 2024 and 6.6% in 2025.
About Asian Development Bank
- Established: December 19, 1966
- Mission: Foster economic growth and cooperation in the Asia-Pacific region
- Functions:
- Provides loans, technical assistance, grants, and investments for social and economic development.
- Finances private sector projects and public-private partnerships.
- Facilitates policy dialogues and offers advisory services.
- Arrange co-financing with various institutions.
- Headquarters: Manila, Philippines
- Members: 68 (49 from Asia-Pacific, 19 from elsewhere)
- Control: Board of Governors representing member countries (similar voting system to World Bank).
- Source of Funding: It relies on member contributions, retained earnings from lending, and the repayment of loans for the funding of the organisation.


 World Autism Awareness Day 2025, Theme, ...
World Autism Awareness Day 2025, Theme, ...
 Utkal Divas 2025: Odisha Foundation Day ...
Utkal Divas 2025: Odisha Foundation Day ...
 International Days List of 2025, Importa...
International Days List of 2025, Importa...





















