Table of Contents
Context
- A complaint of sexual harassment has been lodged in Kolkata against the Governor of West Bengal, C V Ananda Bose.
- However, due to Constitutional immunity, the police are prohibited from listing the Governor as an accused or conducting an investigation into the case.
Article 361 of the Indian Constitution
- Constitutional Immunity for Governors: Article 361 of the Indian Constitution provides that neither the President nor Governors can be held accountable in any court for actions performed in the course of their duties.
- It specifically prohibits criminal proceedings against them during their term of office and also prevents their arrest or imprisonment during this period.
- Supreme Court Ruling in 2006 (Rameshwar Prasad v Union of India): The Supreme Court affirmed the full immunity granted to Governors, protecting them from legal action even if allegations of personal misconduct are made.
- Historical Precedents of Immunity:
- In 2017, criminal conspiracy charges were allowed against several BJP leaders and the Governor of Rajasthan Kalyan Singh.
- The Supreme Court clarified that Kalyan Singh while serving as the Governor of Rajasthan, was “entitled” to immunity under Article 361 of the Constitution.
- The Court also noted that charges would be brought against him by the Court of Sessions once he no longer held the position of Governor.
- In 2017, Meghalaya’s Governor V Shanmuganathan resigned following prompts from the Central Government after being accused of sexual harassment by staff at Raj Bhavan.
- In 2009, N D Tiwari, the then Governor of Andhra Pradesh, resigned citing “health grounds” amidst allegations of involvement in a sex scandal at Raj Bhavan.
- In 2017, criminal conspiracy charges were allowed against several BJP leaders and the Governor of Rajasthan Kalyan Singh.
POSH Act
- The “POSH Act” in India refers to the Sexual Harassment of Women at Workplace (Prevention, Prohibition and Redressal) Act, 2013.
- This legislation was enacted to ensure that women are provided a safe working environment and are protected against sexual harassment at all workplaces, be it in the public or private sector.
- The Act was introduced following the landmark judgement of the Supreme Court in the Vishaka vs. State of Rajasthan case in 1997.
Workplaces Covered Under the Law
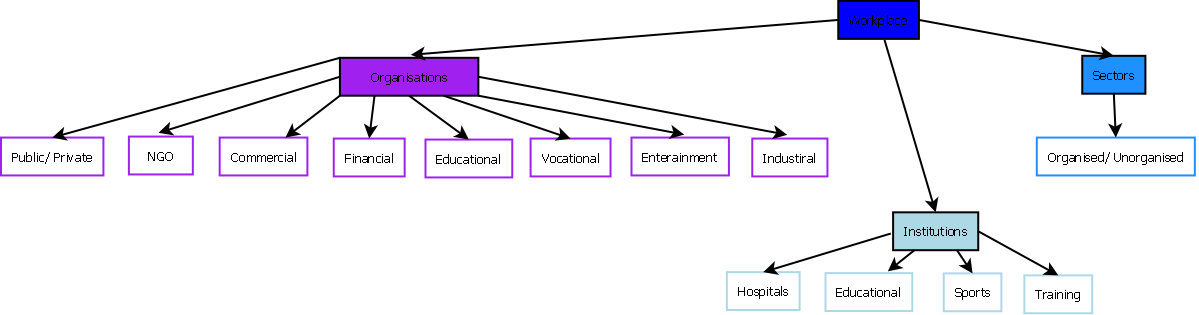
| About POSH Act | |
| Definition of Sexual Harassment | Includes unwelcome acts or behaviours such as physical contact, requests for sexual favours, and other unwelcome conduct of a sexual nature. |
| Coverage | Applies to all workplaces and covers all women, irrespective of their age or employment status. |
| Committees |
|
| Duties Of Employers | Includes providing a safe working environment, organising awareness programs, and assisting in the proceedings under the Act. |
| Redressal Mechanism |
|


 Utkal Divas 2025: Odisha Foundation Day ...
Utkal Divas 2025: Odisha Foundation Day ...
 List of Military Exercises of India 2024...
List of Military Exercises of India 2024...
 GPS Spoofing and Its Impact in India: A ...
GPS Spoofing and Its Impact in India: A ...





















