Context: India records an estimated 58,000 snakebite deaths annually, making it the “snakebite capital” of the world.
What are Antivenoms?
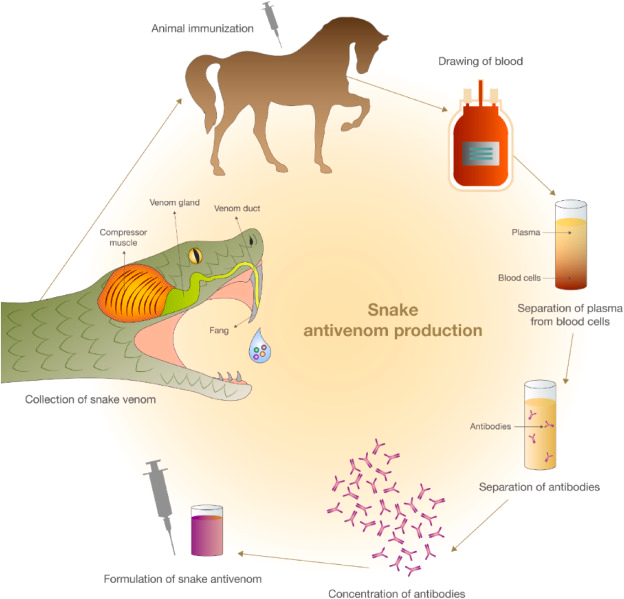
- Antivenoms (or antivenins) are life-saving medicines used to treat snakebites. They work by neutralizing venom toxins in the body.
- Production: Animals like horses are injected with small amounts of venom to stimulate antibody production. These antibodies are then harvested and purified to create antivenoms.
- Function: Antivenoms bind specifically to venom toxins, neutralizing their effects and allowing the body to clear them.
Snake Venom Composition
- It is a lethal cocktail of toxic proteins evolved to immobilize prey and defend against threats.
- Types of Toxins:
- Haemotoxins: Destroy blood cells and disrupt clotting.
- Neurotoxins: Block nerve signals, causing paralysis.
- Cytotoxins: Dissolve tissue at the bite site.
Challenges in accessing Anti-venoms
- Access Challenges: Remote areas lack healthcare facilities with antivenoms.
- Infrastructure Issues: Cold storage is critical for antivenom preservation, its non-availability in rural areas is an issue.
- High manufacturing costs
Future of Antivenoms
- Researchers use recombinant DNA technology to produce lab-engineered, synthetic antivenoms free from animal-derived proteins and offer greater safety and efficacy.
| Data on Snakebites in India |
|


 India Shot Down Pakistani F-16 Jet Amid ...
India Shot Down Pakistani F-16 Jet Amid ...
 Akashteer System, Purpose, Benefits, Sig...
Akashteer System, Purpose, Benefits, Sig...
 Total Blackout in Jammu and Kashmir Afte...
Total Blackout in Jammu and Kashmir Afte...





















