Table of Contents
More on Anti-Biotic Resistance News
- A study in 2019 found that more than 1 million people a year died from infections linked to microbes that are resistant to antibiotics. This was more than deaths caused by Malaria or HIV/AIDS.
- Experts have identified antibiotic resistance as one of the greatest challenges facing humanity. If the problem remains unsolved, 10 million people could die as a result by 2050.
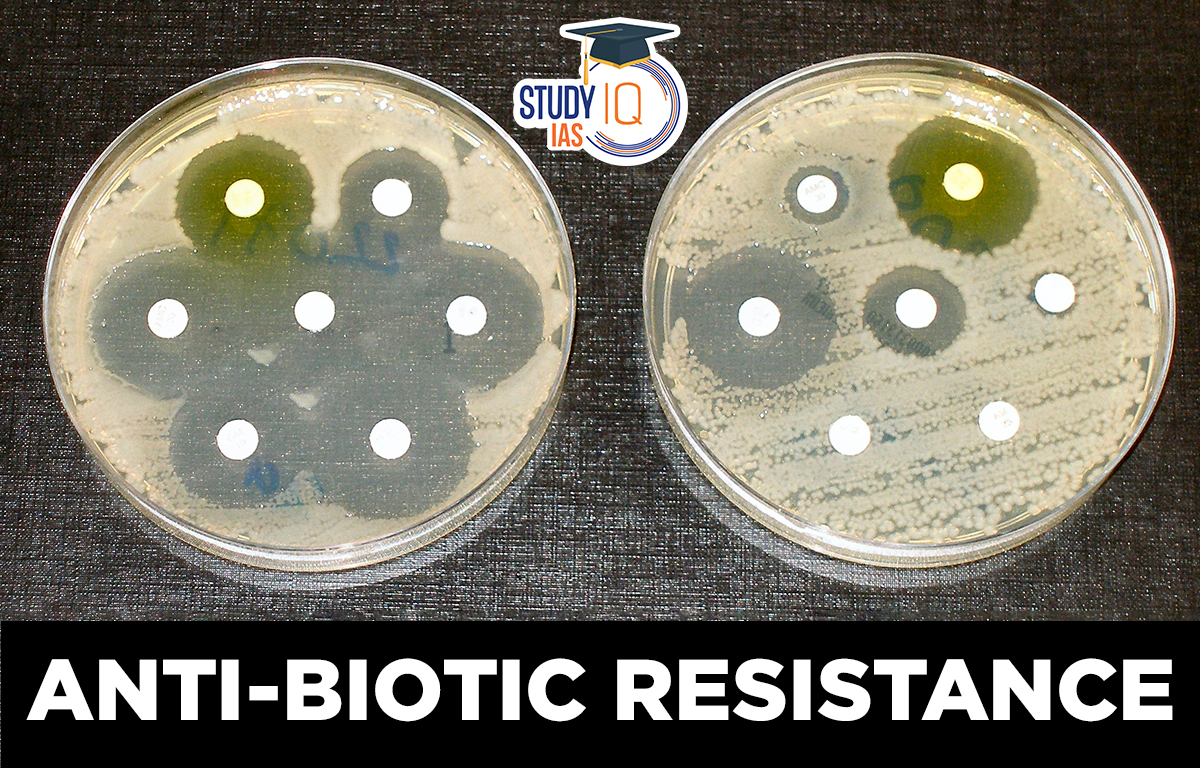
What is Anti-biotic Resistance?

- Anti-biotic resistance is a type of Anti-Microbial Resistance in which certain types of bacteria become resistant to anti-biotic drugs.
- Reasons: The main reason for anti-biotic resistance is overuse and misuse of antibiotics. More we use antibiotics, the worse the problem of antibiotic resistance becomes.
- Mechanism: Antibiotics work by binding to a specific target protein on a bacterium, then entering to kill it from the inside. Bacteria escape by:
- Mutations: Bacteria evade antibiotics through mutations that allow them to stop drugs from binding to bacterial proteins, thus preventing their demise.
- Protein production: Bacteria can also achieve resistance by producing proteins that inactivate or modify the antibiotic compound.

Tackling the Problem of Anti-Biotic Resistance
- Antibiotic resistance will be difficult to be completely eradicated as it is the nature of evolution by natural selection that allows bacteria to find ways to evade antibiotics. However there are some methods such as:
- Modifying existing anti-biotics: Scientists have to continuously modify old antibiotics so that they overcome resistance.
- For example, Penicillin and cephalosporin antibiotics have undergone many rounds of modifications to improve their drug-like properties and overcome resistance.
- However, this is more of a delaying tactic than fundamentally fixing the core issue of antibiotic resistance. The new compound in future could have poor drug-like properties or toxicities.
- Develop new anti-biotics: Making brand-new drugs hasn’t been very successful in recent decades. Majority of the chemicals currently being used in human drugs were discovered in the mid-1980s
- Recently, there are some signs of progress due to sophisticated drug discovery technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI).
- Machine learning and computer simulations have helped scientists to check the efficacy of the drugs.
- Regulating anti-biotic use: Experts have demanded regulation of antibiotics so their use is limited to situations when they are strictly necessary.
- This move is expected to slow down antibiotic resistance while drug discovery catches up.
- Limiting the use of antibiotics in agriculture and poultry would also have a major impact on reducing anti-biotic resistance.
Way Forward
- Investments in drug discovery: Many large companies working on new antibiotics have abandoned their projects due to commercial considerations. Smaller companies have failed financially before their candidates reached the clinic.
- There is a need to increase funding for research focusing on anti-biotic drugs. Private donations and government support can help sustain new research.

 The Lancet Commission on a Citizen-Centr...
The Lancet Commission on a Citizen-Centr...
 Basant Panchami 2026: Saraswati Puja, Mu...
Basant Panchami 2026: Saraswati Puja, Mu...
 Parakram Diwas 2026: Significance, Histo...
Parakram Diwas 2026: Significance, Histo...

























